Class Mammals or Animals
OPTION 1
A1. Maintaining a constant body temperature is characteristic of
2) hedgehog
4) turtles
A2. The beaver has a body covering
1) hair
2) feather
3) chitinous
4) scaly
AZ. The horse's hoof is a modified area
1) skin
2) foot bones
3) phalanges of the finger
4) leg bones
A4. Complication nervous system mammals is expressed in an increase
1) cerebral cortex
2) medulla oblongata
3) spinal cord
4) nerve nodes
A5. Unlike birds in digestive system mammals available
1) esophagus
3) a set of teeth
4) pancreas
A6. The four-chambered heart in the circulatory system has
1) lizard
2) dog
3) frog
B1.
A. Among mammals, a subclass is distinguished Oviparous, which reproduce by eggs (platypus and echidna).
B. Representatives of different orders of mammals differ in the structure of the dental apparatus.
1) Only A is true
2) Only B is true
3) Both statements are correct
4) Both judgments are wrong
B2. Choose three true statements. Representatives of the order Pinnipeds are mammals
1) seal
2) dolphin
4) walrus
5) fur seal
6) shark
BZ.
FEATURE OF LIFE
A. The act of double breathing (gas exchange during inhalation and exhalation)
B. Feeding babies with milk
D. Bearing a cub in the body of a female
ANIMAL CLASS
1) Mammals
B4.
1) Amphibians
4) Reptiles
Answer: 3, 1, 4, 2.
IN 1. Task to work with figure 7.
A, What animal organ system is shown in Figure 7?
1) digestive
2) circulatory
3) respiratory
4) nervous
B. What function is provided by the organs indicated in Figure 7 by the number 1?
1) digestion
2) reproduction by eggs
3) egg maturation
4) the act of double breathing
IN. The organs indicated in Figure 7 by the number 2 are involved in
1) heartbeat
3) movement of food
4) urine formation
OPTION 2
A1. Feeding babies with milk
1) penguin
2) crocodile
4) fox
A2. The sebaceous and sweat glands are found in the skin
1) proteins
2) lizards
3) penguin
4) partridges
A3. Unlike reptiles, in the skeleton of mammals it changes significantly in structure.
1) skulls
2) leg bones
3) belts of the upper limbs
4) tail spine
A4. Unlike reptiles, the mammalian hearing organ includes
1) middle ear
2) eardrum
3) auricle
4) cochlea of the inner ear
A5. gas exchange organ in respiratory system dogs serves
1) alveolar lungs
4) larynx
A6. During the development of the embryo in animals, the placenta, or baby place, is formed in
1) uterus
2) ovary
4) testis
B1. Are the following statements true?
A. Representatives of the order Cetaceans - dolphins and whales - breathe with gills.
B. In marsupial mammals (kangaroo, possum), cubs are born underdeveloped, and their further development occurs in the mother's pouch.
1) Only A is true
2) Only B is true
3) Both statements are correct
4) Both judgments are wrong
B2. Choose three true statements. Members of the rodent order are
2) beaver
3) jerboa
4) bat
6) rat
BZ. Establish a correspondence between the feature of life activity and the class of animals for which it is characteristic.
FEATURE OF LIFE
A Maintaining a constant body temperature
B. Reproduction by eggs or ovoviviparity
B. Unsteady body temperature
D. Most representatives are characterized by live birth
ANIMAL CLASS
1) Reptiles
Write down the corresponding numbers in the table.
B4. Establish the sequence of occurrence in the course of evolution of classes of chordates.
1) Reptiles
3) Mammals
4) Amphibians
Answer: 2, 4, 1, 3.
IN 1. Task to work with figure 8.

A. What animal organ system is shown in Figure 8?
1) digestion
2) blood circulation
3) breathing
4) nervous
B. The systemic circulation originates in
1) left ventricle
2) right ventricle
3) right atrium
4) left atrium
IN. Through the vessels of the small circle, blood enters the
1) lungs
3) stomach
4) skeletal muscles
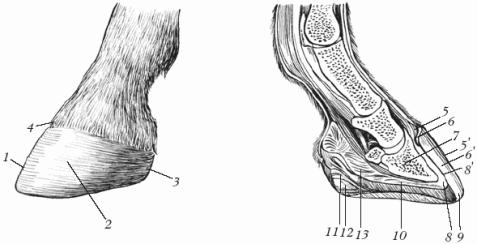
Hooves are located on the third phalanx of the third finger of equids, including horses. The hoof is a hard skin tip that protects the end of the toe from injury. The hoof is an area of skin, the epidermis of which in certain places produces stratum corneum of various structure and consistency. Therefore, according to the location and nature of the stratum corneum produced, the following 4 parts are distinguished on the hoof: border, rim, wall and sole (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. The structure of the horse's hoof: (Fig. Left - outside view): 1 - hook part; 2 - lateral side wall; 3 - heel part; 4 – rim area; (fig. on the right - view: sagittal median section): 5 - three layers of the border; 5 - glaze; 6-3 layers of whisk; 6 - tubular horn; 7 - coffin bone; 8 - dermis of the hoof wall; 8 - white leafy horn; 9 - white line; 10 - sole dermis; 11 - crumb horn; 12 - crumb dermis; 13 - elastic cushion of the crumb

Hoof border - a narrow strip on the border between the hairy skin and the underlying hoof rim; connects the hairy skin with the horny capsule and softens the pressure of the pointed top of the horny capsule. The corolla is located below the border, covering the tendon of the finger in front, and the lateral cartilages on the side. The hoof wall, the most massive part of the hoof, covers the coffin bone and lateral cartilage. There are 3 stratum corneum on it - glaze, tubular horn, leaf horn. The end section of the latter forms a white line, which is a guideline when shoeing horses (it is insensitive, so nails are hammered along it). The hoof sole is a concave plate with a conical notch for the digital cushion, located on the underside of the hoof. The thickness of the horn of the sole is not constant, as it is erased when walking.

Rice. Fig. 2. Horse hoof (bottom view): a - horny wall; b - sole and frog; 1 - inversion part; 2 - heel angle; 3 - side part; 4 - hook part; 5 - arrow; 6 - sole; 7 - white line
In riding horses, the hooves are denser, with an elastic horn, in heavy trucks they are loose, the hoof horn is soft. Disadvantages and defects of the hooves are due to their irregular shape, poor-quality horn, incorrect positioning of the legs, and poor hoof care. Many of them lead to lameness. Crumbs. These are the supporting parts of the limbs. They are rich in nerve endings, due to which they play the role of an organ of touch. Horses have a digital cushion, which has the shape of a wedge forked by a gutter. It consists of a pillow, arrow and cartilage (Fig. 2) and acts as a spring that softens shocks when leaning on the ground.
A basic level of
For each question, choose one correct answer from the four given.
A1. Maintaining a constant body temperature is characteristic of
- turtles
A2. The beaver has a body covering
- hair
- feather
- chitinous
- scaly
AZ. The horse's hoof is a modified area
- foot bones
- finger phalanges
- lower leg bones
A4. The complication of the nervous system of mammals is expressed in an increase
- cerebral cortex
- medulla oblongata
- spinal cord
- ganglions
A5. Unlike birds, the digestive system of mammals contains
- esophagus
- liver
- set of teeth
- pancreas
A6. The four-chambered heart in the circulatory system has
- lizard
- dog
- frog
- perch
- - - Answers - - -
A1-2; A2-1; A3-1; A4-1; A5-3; A6-2.
Increased difficulty level
B1. Are the following statements true?
A. Among mammals, a subclass is distinguished Oviparous, which reproduce by eggs (platypus and echidna).
B. Representatives of different orders of mammals differ in the structure of the dental apparatus.
- Only A is true
- Only B is true
- Both statements are correct
- Both statements are wrong
B2. Choose three true statements. Representatives of the order Pinnipeds are mammals
- seal
- dolphin
- fur seal
- shark
BZ. Establish a correspondence between the feature of life activity and the class of animals for which it is characteristic.
Feature of life
A. The act of double breathing (gas exchange during inhalation and exhalation)
B. Feeding babies with milk
B. Ligaments located in the trachea are involved in the formation of the voice
D. Bearing a cub in the body of a female
Animal class
- mammals
- Birds
Write down the corresponding numbers in the table.
B4. Establish the sequence of occurrence in the course of evolution of classes of chordates.
- Amphibians
- Birds
- reptiles
- - - Answers - - -
B1-3; B2-145; B3-2121; B4-3142.
The coffin bone in a horse is a kind of shock absorber that prevents injury when moving. Therefore, it is the main functional component of the animal's body, affecting its health and performance. Horses distribute weight efficiently, providing better grip on the ground, allowing the structure of the horse's hoof.
Ground grip
What is a hoof
The hoof is a keratinized capsule that protects the tip of a horse's toe from damage and is similar to the claws of wild animals and human nails. Horse hooves require careful care. Incorrect positioning or incorrect shape of the legs from birth leads to serious injuries, for example, and diseases.
The horse's hoof structure is special, because the thickness of the stratum corneum of the hoof varies in some areas. In its composition are distinguished:
- sock;
- heel;
- sole;
- crown ring;
- arrow;
- corner;
- side wall;
- heel wall;
- hook wall.
It is easy to find a coronal ring in the structure of the horse's hoof. It is located at the hairline. The hoof bone and lateral cartilages are covered by a horny wall, consisting of:
- glaze;
- tubular horn;
- leaf horn.
 parts of the hoof
parts of the hoof The sole of the hoof in horses differs from other parts in that it does not have a stratum corneum. It consists of a horn arrow and a white line. The horn arrow is needed to prevent slipping. It is located in a wedge between the legs of the sole. The white line consists of insensitive fabrics, therefore it is suitable for driving in when forging nails. If the condition of the hooves is not monitored, it can develop, leading to a serious limb problem.
The front and back hooves of a horse differ in shape and size. The rear ones are smaller than the front ones, the sole is concave inward. The front hooves have a larger frog and a low calcaneus.
Periodically, horses cut their hooves, as the hoof horn grows. Hoof trimming corrects foot placement and properly distributes weight. The hooves are also trimmed before forging for a good fit of the horseshoe to the sole. Occasionally, hoof trimming is done for medical reasons and for some diseases of horseshoes.
 Hoof after cleaning
Hoof after cleaning Horses of riding breeds have dense hooves, the horn is elastic, and the draft horse has a loose hoof, the hoof horn is soft.
The difference is also visible in size - the heavy truck has a larger hoof. The shape of the hoof is also different: the heavy truck has flat walls and a low heel, while the horse has round walls and a high heel.
At the hooves different kinds colors: dark, light, striped and mixed. But the dark ones are considered the strongest hooves.
A simple horse's hoof has many functions, which is why good hoof care is so important.
The horse's leg is dressed in a strong horn shoe - a hoof. This important organ provides the horse with stability, fast running and protection from enemies.
Eohippus
The lower part of the horse's leg is its only toe, and the hoof is a modified, overgrown nail.
Have horses always had such legs and such hooves? The Russian scientist V. O. Kovalevsky (1873) proved that the ancient ancestors of horses had a five-fingered limb.
About 50 million years ago, the middle strip of the Northern Hemisphere was covered with lush tropical forests, inhabited by Eohippus, the ancestor of modern horses. 
Orohippus
He was about the size of a fox and had five toes on his feet, of which only 3-4 touched the ground. Eohippus hid in the forest thickets and ate vegetation.
The climate on earth changed, and in connection with it, the living conditions of plants and animals. Steppes with herbaceous vegetation were formed. Living in open places, the ancestors of the horse learned to run fast so as not to fall into the clutches of predators. 
Mesogippus
Side fingers were superfluous. The body was supported by the middle toes.
The four- and three-toed ancestors of horses that lived in North America: orogippus 38 centimeters tall and mesogippus, longer-legged, already about 60 in height. In those days, the American and Asian continents were connected to each other. On the site of the Bering Strait, animals easily moved from the western to the eastern hemisphere. 
Merikgippus
The primitive horses in America died out about 30 million years ago, and their descendants moved to Asia. Merikgippus is already very similar to a horse, but has three more toes on its feet.
Modern horses do not have three-toed. But, comparing the skeletons of the horse and its ancestors, one can see two thin bones adjacent to the metatarsus. This is nothing more than the remains of an ancient horse "paw".



