To keep your hands thin and beautiful, you need to do special exercises. Get 4 effective workout programs and get your hands in perfect shape without leaving home!
Beautiful, embossed arms, impeccable chiseled shoulders, toned muscles are the dream of many women. However, when working on their figure, many girls do not pay due attention to their hands, fearing to “pump over” and look masculine. Fitness instructors assure that these fears are groundless due to differences in hormonal balance. The male hormone responsible for muscle growth is testosterone. In women, estrogen predominates, which means that even with strength exercises and working with large weights, the ability to build muscle mass will be limited and the girl will never come close to male proportions. Therefore, effective training for the muscles of the hands must be part of the program.
Arm Slimming Workouts
Due to the increased content of estrogen, women tend to be overweight. Therefore, training is necessary to maintain metabolism, muscle tone and create a proportional figure. Where to train? You decide. You can do simple exercises to keep your muscles in good shape at home. There are techniques that allow you to work with no weight or with little weight (water bottles, small dumbbells, books), but exercising in the gym, you can achieve amazing results in less time.
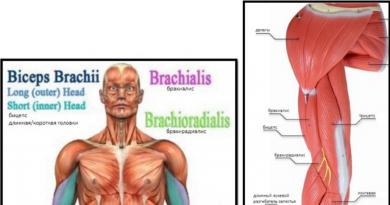
During arm training, the following muscle groups are worked out:
- biceps (flexor);
- triceps (extensor);
- shoulder delta;
- forearm.
When developing a program, you must follow simple rules
Warm up
Before any workout, you need to warm up the muscles to eliminate the possibility of injury. A couple of exercises will be enough.
There are two opinions about how much weight you need to work with. The first is low weight and high reps, the second is high weight and several small supersets in a row. The first option is ideal for the home. Multiple repetitions make it possible to burn excess fat, so the weight should allow you to perform the exercise for the recommended number of times. It is recommended to increase the number of repetitions as soon as you realize that you can easily cope with the load. The second option (working with weights and shells) is possible only in fitness centers.

For training hands in the gym, it is recommended to choose large weights. This guarantees the best return. The result is manifested after the weight of the dumbbells reaches 7-8 kg. This does not mean that you immediately need to start with “explosive weight”, but it is also not recommended to “get into the taste” with dumbbells of 1-2 kg for a long time. According to instructors, the optimal weight for a beginner is 5 kg.
How to choose the right weight: start doing a set of exercises and if after the third set you feel tired, then this weight is right for you.
Program
Schedule a set for the week. The number of sets and repetitions depends on how you feel. It is also necessary to make an adjustment for the days of the cycle. To drive away subcutaneous fat from the hands, 25-30 repetitions are enough.
The optimal duration of a workout is 45 minutes. It is advisable to monitor the pulse (the norm is 130 beats per minute). When exceeding the norm, it is better to stop exercising.
Proper Completion
You need to finish the workout with the so-called "hitch".
Do not train more than 3 times a week, otherwise it will be very difficult for the muscles to recover.
At home
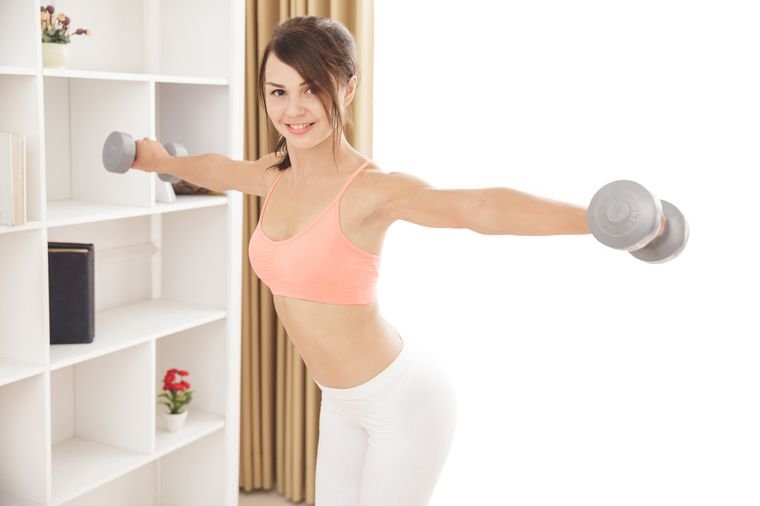

1. Complex one
For him, you will need dumbbells or bottles of sand (water). Start with 12 repetitions and gradually increase their number.
Warm up
- Raise your hands up one at a time (starting with the right). Then, lower down, bending them at the elbows, while the fingers are clenched into a fist. We repeat, only now the left one starts.
- Stretch your arms out in front of you, interlock your fingers and stretch slightly. Feel the stretch in your back muscles.
- Everyone knows the "mill". The back is straight, the buttocks and stomach are “tightened”, the legs are shoulder-width apart, the feet are parallel to each other. Take turns rotating your straight arms in a circle for 40 seconds.
- Jumps and swings. Feet together, arms loose. Perform jumps (legs to the sides) and at the same time raise your arms up (they also spread apart). Jump at a fast pace for 40-45 seconds.
1.1 Exercise for the arms and shoulder muscles
Starting position (IP) for all exercises: feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent, back straight, stomach pulled in.
Take dumbbells, bend your arms at the elbow joint so that a right angle is formed. In this position, spread them apart (while the elbows rise to shoulder level), count to two and then slowly lower, returning to the PI. This is a great exercise to get the ovens in the best possible shape. Exhale as you lift the dumbbells.
1.2. Work with biceps
Turn your hands palms forward, bend them, press your elbows to your sides and raise the dumbbells. Squeeze your hands as you lift and tighten your biceps.
Bend your elbows as you raise the dumbbells in front of you. Raise dumbbells to shoulder level.
1.3. Work with triceps
PI for this exercise: Bend your knees slightly and tilt your head forward. Keep your back straight.
Standing in the IP, bend your arms and linger in this position. On the count of two, straighten them back and then bend them back. Don't forget to tighten your belly. Make sure that the neck is not tense.
After doing the exercise 12 times, straighten your arms and linger in this position for 8 counts.
1.4. Triceps relaxation
Performed without dumbbells. Bend your right arm at the elbow and bring it behind your head with your left. Hold for three seconds and then switch sides. Feel your triceps relax.
1.5. Push ups
Emphasis on the knees and palms, the stomach is tightened. Get down and up for a count of two. We do not strain the neck, the navel is pulled up. Push up from the floor 12 times. Keep your back straight, breathe evenly.
After completion, sit on your heels, palms remain on the floor, stretch your back, relax.
1.6. For upper back and shoulders
Lie on your stomach, stretch your arms bent at the elbows in front of you so that they form a right angle. Slowly lift up, just above shoulder level and slowly lower down. It's great for correcting posture.
1.7. "Hitch"
Each exercise must be repeated 10 times.
Hands on the belt. At the expense of "one" - turn to the right and spread the arms to the sides, at the expense of "two" - return to the IP. On the count of three, turn left.
Hands spread apart, make circular swings with both hands at the same time.
2. Complex second
2.1. Starting position (IP): feet shoulder-width apart, knees straight, back straight, stomach pulled in, arms down.
Spread your arms with dumbbells to the sides. Number of repetitions: 30.
2.2. IP: sitting on a chair, back straight, legs together.
Raise your arms with dumbbells up, gently bend your arm, winding the dumbbell behind your head, and then unbend it. Number of repetitions: 20.
2.3. IP: see exercise 2.1.
Spread your arms to the sides, lock in this position for two counts and lower. Number of repetitions: 30.
2.4. IP: see exercise 2.1.
Raise your hands in front of you, fix in this position for two counts, slowly lower. Number of repetitions: 30.
In the gym
Girls are recommended to start working in the gym with basic exercises for the hands. For beginners, this is the foundation of the basics. This is free weight (dumbbell or barbell) work that aims to build muscle mass and is a must for beginners and experienced bodybuilders alike.
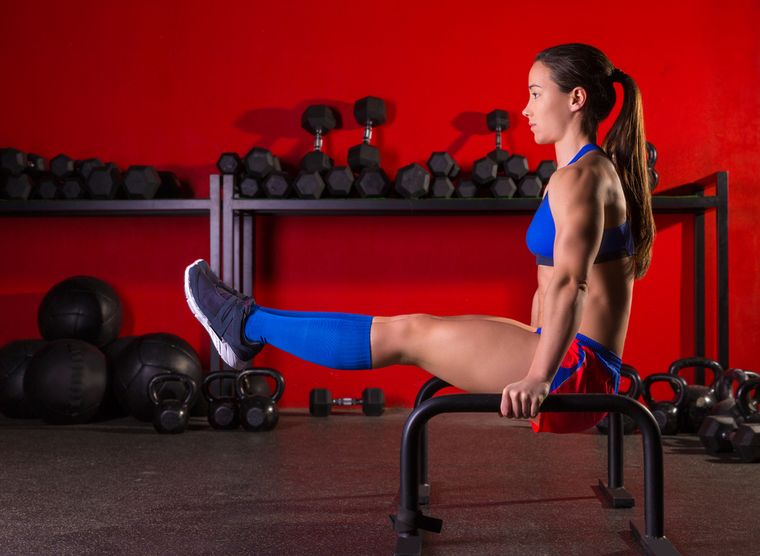

1. Basic exercises (BU) for hands
1.1. Push-ups from the bars
One of the most complex, but effective BU. When it is performed, not only the triceps are involved, but also the pectoral muscles. Beginners are engaged with their own weight, "advanced" athletes can use weight belts. Not every girl can lift her weight, so if the bars do not give in to you, do not despair. Strengthen your arms with other available BUs, and return to the uneven bars after a couple of months of regular training.
What is important in the uneven bars: the right technique. If done incorrectly, there is a risk of injury. To prevent this from happening, do not start the exercise from the bottom point. For unheated muscles, this is fraught with ruptures and sprains. Lock on outstretched arms and slowly lower yourself down. Watch your elbows. Some should be laid back and as parallel as possible. So the extensor muscles are better worked out.
Little tricks: for maximum triceps work, do not lean too much and keep your shoulders parallel to the bars and your elbows back. To train the pectoral muscles, the elbows should look to the sides, and the body should only lean forward slightly.
Number of repetitions: the maximum possible for you. When the next full ascent is not possible, slowly descend to the bottom point and rise again to the highest possible height. Repeat two more times.
1.2. Pull-ups on the classic horizontal bar
Works both biceps and back. To use different muscle groups, you can change the grip ("from yourself" and "for yourself").
Number of repetitions: as many as you can do. And as usual, after reaching the “limit”, try to pull yourself up one more time or two.
Many modern gyms are equipped with a special simulator (gravitron) that makes it easier to perform push-ups and pull-ups. The load in the gravitron is reduced by a counterweight, which starts working when a person needs help. Thus, there will be no risk of breaking the lower back, the muscles gradually get used to the load and become stronger.
1.3. seated french press
With this technique, the triceps receive a noticeable load. It is important to do everything right and follow the neck. When working with large weights, it is better to ask the coach for insurance.
IP: The bench press is performed from a horizontal bench with a back. Grasp the dumbbell so that the disk is in the palm of your hand and your thumbs are on the handle. Raise it above your head with both hands. The forearm should be next to the head, perpendicular to the floor. Inhale and slowly lower the dumbbell behind your head in a semicircular path. As you exhale, fully extend your arm and return the dumbbell to its original position.
When performing a bench press, it is very important to monitor the condition of the shoulders and elbow joints. They should be motionless, and the amplitude of their movement should be maximum.
1.4. Lifting dumbbells for biceps while standing
IP: feet shoulder-width apart, knees straight, elbows pressed to the body, arms with dumbbells lowered down. The wrists need to be turned so that the palms “look” forward.
As you exhale, slowly bend your arm until the biceps is fully contracted. Dumbbells should be at shoulder level. Hold for a couple of seconds and as you exhale slowly return to the PI.
Alternatively, such an exercise can be performed while sitting or bending your arms alternately (this will make it possible to work with more weight).
1.5. Lifting the handle (for biceps)
It is performed on the lower block with a straight handle.
IP: feet shoulder-width apart, back straight, buttocks tense, stomach pulled in. The elbows are pressed to the body. On exhalation, we raise the handle to tension at the top point (the so-called "peak of the biceps") and slowly lower it down while inhaling. At the same time, we do not unbend our arms to the end in order to maintain static tension.
1.6. Lowering the handle from the upper block (to the triceps)
Helps triceps muscles to gain shape, tone and become more prominent.
IP: feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent, elbows pressed to the sides. Bend your lower back, grab the handle of the upper block. As you exhale, pull it down until you get maximum tension in the extensor muscle and press your elbows to the sides of the body. Then slightly tilt the body forward and fully straighten your arms due to the tension of the triceps. Hold for a moment and slowly return to the PI as you inhale.
Concentrate on the work of the muscles.
Alternatively, lowering from the upper block can also be done with a rope handle. In this case, lowering your hands, you should slightly spread them apart at the bottom point of the movement.
2. Additional exercises
2.1. Extension of the arm with the use of a rubber shock absorber (for triceps)
IP: sit down, straighten your back. Take the elastic so that one bent arm is behind the head, and the other is wound behind the back. The elbow should be as close to the head as possible.
As you inhale, straighten your arm, stretching the rubber shock absorber, and as you exhale, return to the PI. Perform 20-25 repetitions. When doing this exercise, try not to use momentum. Work with the expander is performed only with muscle effort. Watch your elbow and do not deviate it to the side. The shoulder must remain motionless.
2.2. Extension of arms with an expander behind the back, standing
This bench press exercise is performed while standing and perfectly stabilizes the muscles of the shoulder blades, shoulder, gluteal muscles.
IP: feet shoulder-width apart, slightly bent. Place the expander behind your back so that it is below your shoulder blades (approximately at chest level). Raise your arms to chest level, bend at the elbows, and keep your palms parallel to the floor. The brushes must be motionless.
From the PI as you exhale, slowly extend your arms in front of you, then return to the PI. The main thing is to control muscle work as much as possible. Do not make it easier for yourself by using the force of inertia, otherwise the efficiency of work will be reduced to zero.
2.3. Bent over arms
During work, the triceps are effectively pumped. It is performed with dumbbells of a weight that is comfortable for you or with an elastic band.
IP: feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent, body tilted forward, eyes looking at the floor. The pelvis should be pulled back, slightly bending the lower back. The back should remain straight. Bend your elbows, lift them back and bring your shoulder blades together. Elbows should always remain parallel to each other.
Perform extensions in three sets of 30-35 times. At the end of each approach, it is necessary to fix the position for 25-30 seconds.
2.4. "Reverse" push-ups
An effective way to tone the triceps.
IP: sitting on the floor, knees bent. Take your hands away from the pelvis by 15-20 cm, rest your palms on the floor (position of the palms: fingers forward), tear your buttocks off the mat. With the effort of the muscles of the hands, push up from the floor, make sure that the elbows are parallel, do not spread them apart.
A small nuance: the position of the hips allows you to adjust the load. The closer to the legs, the easier it is to do push-ups and vice versa, the closer to the arms, the higher the load on the muscles.
Number of repetitions: for beginners, it is enough to complete one set of 20-25 times. For those who exercise regularly in the gym, it is recommended to perform two approaches. Between push-ups, lie down on the floor, stretch your whole body, tighten your muscles, pull in your stomach and stay in this position for 20-25 seconds.
2.5. "Reverse" push-ups from the bench
During execution, the entire triceps is completely worked out.
IP: arms shoulder-width apart, legs slightly bent, back straight.
Slowly lower yourself down while inhaling, bending your arms to a right angle. As you exhale, push up from the bench and return to the starting position. When performing the exercise, do not spread your elbows to the sides. The body should move almost close to the bench.
2.6. Extension of the arm from the chest
Another effective triceps exercise. Performed alternately with each hand.
IP: lie on the floor, bend your knees, feet parallel to each other. Take a dumbbell in your right hand. The elbow should be turned outward. As you exhale, bend your arm at the elbow and bring the weighting agent to your left shoulder. As you exhale, straighten it.
Number of repetitions: 15-20 times.
Then, repeat the same with the left hand.
2.7. Concentrated Biceps Curl
This exercise can be performed in various modifications. One option is the seated IP, when the elbow rests on the knee or on the opposite hand. In another variation, it is performed with a barbell and both elbows rest on the knees. Its peculiarity lies in the extraordinary amplitude of movement during the rise of the projectile and a very powerful peak contraction at the top point. Those. when the projectile is lifted up, the load reaches its maximum, and is not removed. This means that when the projectile is delayed at the peak point, you work out the biceps as efficiently as possible. Such an exercise can be performed both with supination (rotational movement) and without it. When rotating the brush, the dumbbell should be closer to the thumb.
It is important that when working with a projectile, the shoulder is strictly perpendicular to the floor. On exhalation, the arm is bent and the weight is lifted; on inhalation, extension is performed.
Method "21"
Experienced bodybuilders note that isotonic programs become less effective over time. A “plateau” effect sets in, when the muscles get tired, get used to the load, the growth of muscle tissue slows down sharply and the effectiveness of training is reduced to zero. David Carfagno (founder of the Institute of Sports Medicine in Scottsdale, Arizona, USA) proposed an innovative technique that allows you to literally "shake" the muscles and start active processes in the body. The essence of the method lies in the fact that during the same exercise it is necessary to alternate three different amplitudes of motion (AP): lower, upper and full. For any BP, 7 repetitions are performed in each approach.
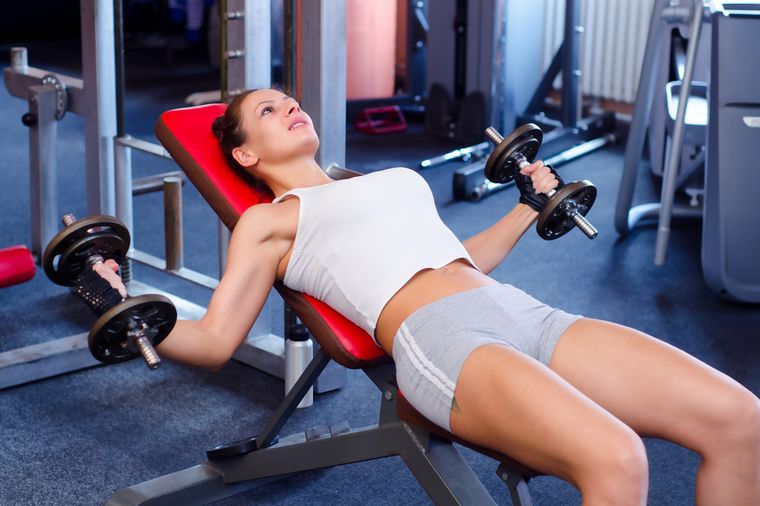

This program is a real test even for endurance bodybuilders, so trainers recommend working with less weight than usual.
Basics
- Arm swing programs consist of three supersets and are performed at a fairly fast pace.
- A minute break is required between sets.
- The first workouts according to the "21" system should consist of one exercise and only one muscle. Gradually, you can diversify the sets and increase the load.
- Any program can be adapted to the Carthagno system.
Scheme of training according to the system of David Carfagno.
1. French bench press
IP: lying on a bench, feet on the floor, parallel to each other, the stomach is pulled in. Hold the dumbbells with your palms facing each other (neutral grip). Straighten your arms and place the weights over your shoulders.
1.1. Lower amplitude: slowly lower the dumbbells to head level. Pause for two counts. Extend your elbows until you reach a 45 degree angle.
1.2. Upper range: Slowly lower the dumbbells until your arms form a 45-degree angle. Pause for two counts. Straighten them out.
1.3. Full range: Lower the dumbbells to head height and then fully extend your arms.
2. Lifting the biceps in the lower block while standing
Performed with a straight crossbar.
IP: feet shoulder-width apart, feet parallel, knees slightly bent, back straight. The crossbar is taken with a “bottom” grip.
2.1. Lower CR: Use your biceps to lift the bar up until your arms form a right angle. Pause for one or two counts, return the crossbar to the PI.
2.2. Upper AD: The bar is compressed to chest level and lowered to 90 degrees.
2.3. Full BP: connect the upper and lower BP.
3. Extension on the block while standing (for triceps)
IP: standing, knees slightly bent, torso slightly tilted forward with a deflection at the waist, elbows pressed to the sides. The bar is held with an overhand grip, the back is straight, the stomach is pulled in. The exercise is performed with the following amplitudes:
3.1. Lower: the crossbar is “squeezed” down by the force of the triceps until the arms are fully extended, then it rises to 90 degrees.
3.2. Upper: the crossbar is squeezed out to 90 degrees and returned to the IP.
3.3. Full: the bar is squeezed towards the floor and then the hands return to the PI.
4. Push-ups
IP: emphasis on socks. The body is straight (parallel to the floor), the stomach does not "sag". Hands shoulder-width apart, fingers pointing forward.
4.1. Lower BP: keeping the body in a straight position, lower the chest to the floor and slowly return to the PI.
4.2. Upper BP: Get down to the floor to the middle of the amplitude.
4.3. Full BP: Fully bend and unbend your elbows, dropping to the floor and rising almost to the level of fully extended elbows.
5. Biceps Curl with Rope Handle
IP: legs together, knees slightly bent, shoulders relaxed, stomach pulled in, arms down.
5.1. Lower amplitude: hold the handle so that the wrists look at each other. Bend your elbows to a right angle and unbend to full extension.
5.2. Upper BP: Bend your arms to the highest point, lower to 90 degrees.
5.3. The projectile moves along the entire amplitude - from the bottom up and descends until the elbows are fully extended.
Drying hands
"Drying" means getting rid of subcutaneous fat and giving the hands a beautiful relief. However, good muscle shape is achieved not only by proper nutrition, but also by physical exercises. Drying is suitable only for those who have already built up good muscles. For beginners, this procedure is strictly contraindicated.

During drying, it is necessary to adhere to the correct proportions of nutrients in the diet. During this period, preference is given to protein foods, and carbohydrates are limited.
In order to dry your hands you need to know the basic rules
- The main emphasis is on short-term aerobic exercise (treadmill, etc.).
- The program should also include work with weight machines aimed at the target muscle group.
- Hand drying exercises are best done in the gym under the guidance of an instructor.
- In addition to dumbbells, during exercises with additional weight, you can use a block simulator, light “pancakes” or a barbell bar.
Contraindications
Despite the seeming harmlessness, hand exercises also have their contraindications. You should definitely consult a doctor if you have the following health problems:
- unstable blood pressure;
- problems with the spine;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- asthma and respiratory diseases;
- obesity;
- osteoporosis, osteochondrosis, etc.;
- diseases of the endocrine system.